Latest Visual Studio 2022 with Copilot should work with below config to preprompt/improve/customizee the Copilot experience.
Source: Adding repository custom instructions for GitHub Copilot – GitHub Docs
My bookmarks and blogposts regarding Software Development in .NET, C#, Angular, JavaScript, CSS, Html
Latest Visual Studio 2022 with Copilot should work with below config to preprompt/improve/customizee the Copilot experience.
Source: Adding repository custom instructions for GitHub Copilot – GitHub Docs
Angular 9 introduced the ng namespace variable, which is available in development mode but not exposed when the application is running in production mode. We can debug an application using that global namespace without any breakpoint or dev tools extension.
Source: Debugging with the ng namespace | Angular Newsletter
A new type of shell
Nu works on Linux, macOS, BSD, and Windows. Learn it once, then use it anywhere.
Nu pipelines use structured data so you can safely select, filter, and sort the same way every time. Stop parsing strings and start solving problems.
It’s easy to extend Nu using a powerful plugin system.
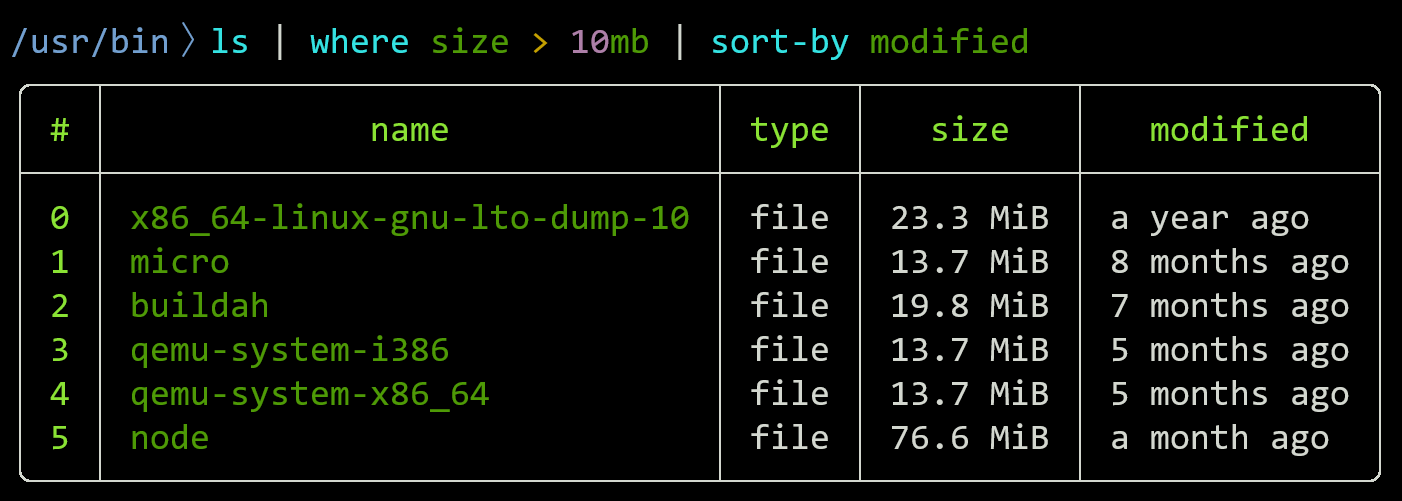
Nu speaks JSON, YAML, SQLite, Excel, and more out of the box. It’s easy to bring data into a Nu pipeline whether it’s in a file, a database, or a web API:
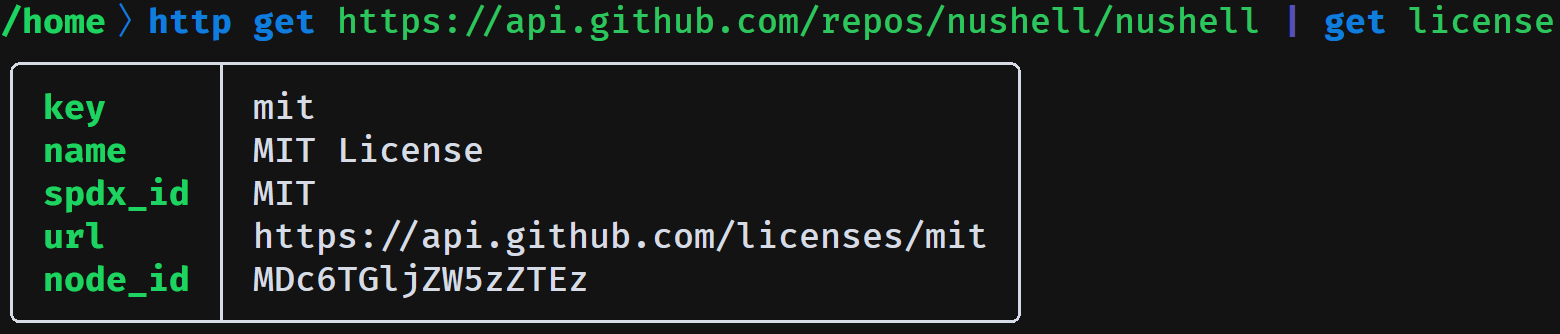
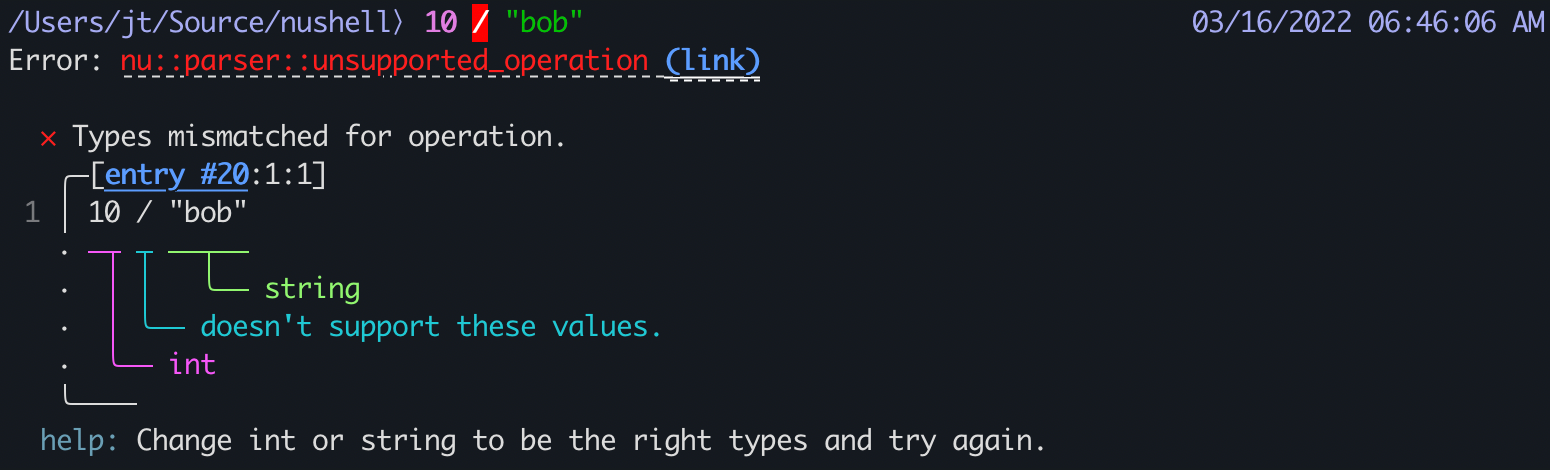
Nu operates on typed data, so it catches bugs that other shells don’t. And when things break, Nu tells you exactly where and why:
Tested in Angular 19.
Add router to component constructor:
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
...
public constructor(
private _router: Router
) {}
Navigate and reload page, even if currently on same url
this._router.navigateByUrl('/', { skipLocationChange: true }).then(() => {
this._router.navigate(['my-page']);
});
Above code navigates to root path without changing url in browser, then navigates to current url /my-page. E.g. “reloads” current page (which has path /mypage).
During web application development, we create solutions that address the customers’ needs and solve problems of businesses and users. To achieve this, different architecture patterns and technologies are used. For many years, application designs have revolved around the In the meantime, there have been a series of advanced frameworks like Flux and Redux, in the same vein, which helps you deal with complex applications. We are aware of the increased complexity in apps that multiplies due to the absence of effective design patterns in place. Here we have compared MVC vs Flux vs Redux to help you create effective, sensible and scalable application architecture.
Continue reading “MVC vs Flux vs Redux: Key Differences Explained”
What is DeepWiki?DeepWiki provides up-to-date documentation you can talk to, for every repo in the world. Think Deep Research for GitHub.
Source: DeepWiki | AI documentation you can talk to, for every repo
I finally understood multithreading — and now my code runs 10x faster. Multithreading used to sound like magic. Or worse — a trap full of race conditions, deadlocks, and endless debugging. But once I broke it down, I realized: It’s just parallel thinking with safety checks. Here’s what helped it all click:
🔹 Threads = multiple tasks running in parallel
🔹 Mutex/locks = only one thread can access shared data at a time
🔹 Race Conditions = when threads clash over shared state
🔹 Deadlocks = when threads wait